STEAM has been around for a while. Because it’s a comparatively new educational concept, how much do you know about it? This blog will break it down for you and let you get to know it better. Read on!
1. What Is STEAM?

STEAM stands for Science, Technology, Engineering, Art, and Math. Though it seems like a compilation of five academic fields, it is really an educational approach to teaching and learning STEM subjects through the arts. Basically, it intentionally integrates academic studies with arts disciplines, for example, visual art, dance, music, and theatre.
2. What Is STEAM Education?
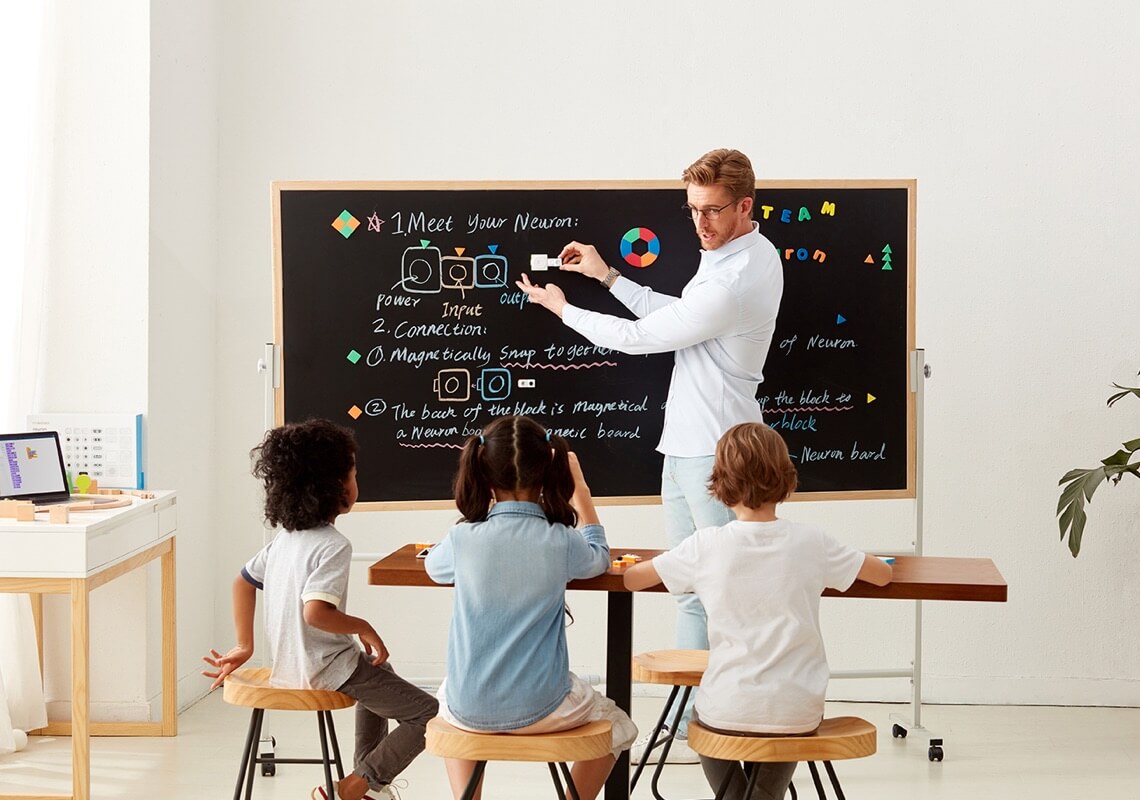

Before STEAM education, there was STEM education, which mainly focused on Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math. But then problems arose and many parents, as well as students, realized that STEM was not enough for their kids’ well-rounded development. The emphasis that schools placed upon STEM did not lead to those dazzling results they’d hoped for, which is when educators started to include the arts as an inseparable component of the educational approach.
With that being said, the idea is not about giving equal or greater time to STEM or the arts. Instead, STEAM (after adding Arts into STEM) education aims to incorporate artistic topics, skills, and ways of thinking to teaching and learning technical subjects.
3. Why Are Robots Used in STEAM Education?
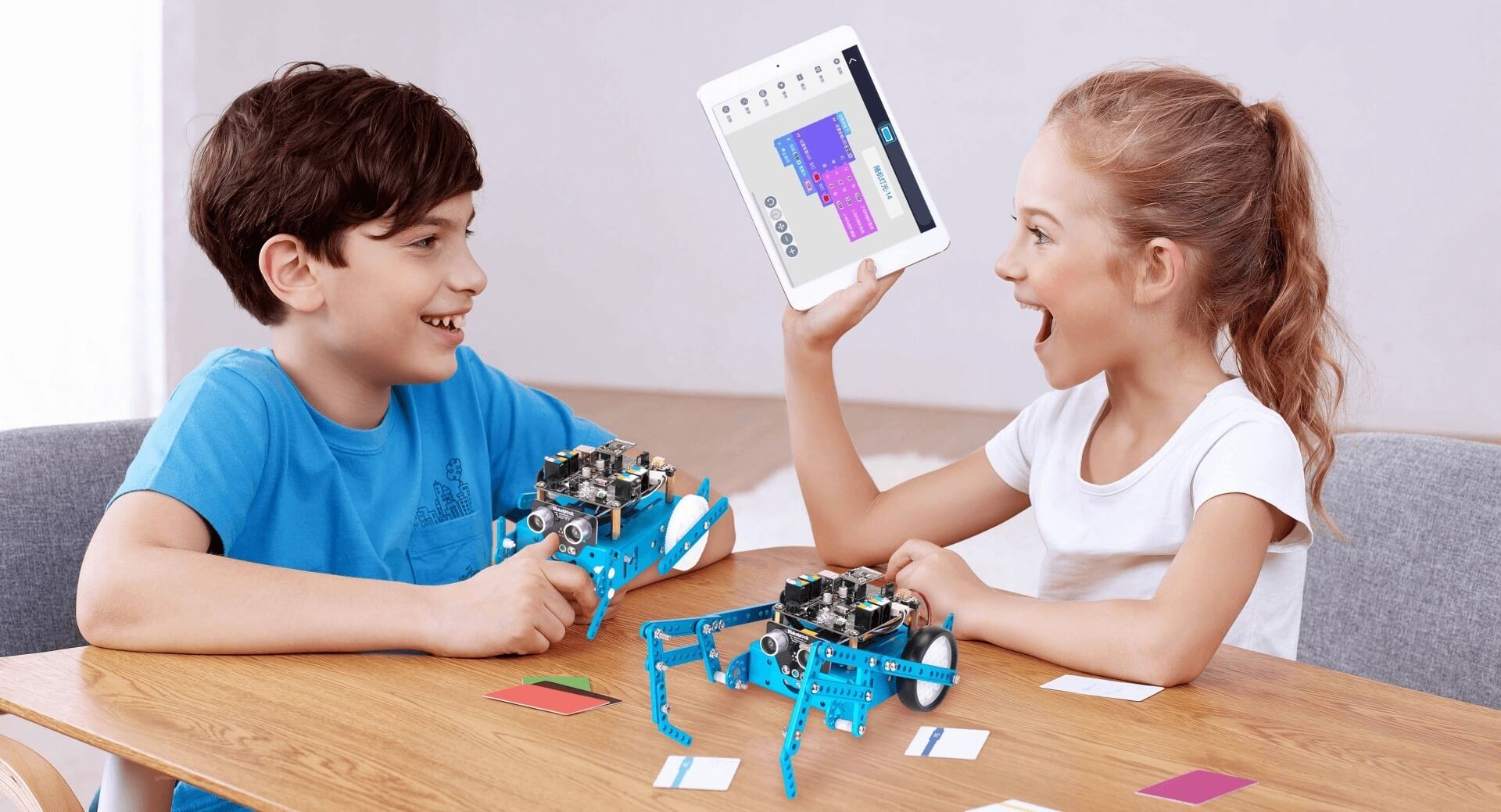

What are we talking about when we talk about robots? You are probably thinking about robots in The Terminators or the little guys that explore the Moon for us, but robotics in STEAM education are so much more kid-friendly and were built to serve educational purposes.
Robots play a crucial role in early STEAM education for kids in both straightforward and subtle ways. First, robotics in STEAM education can provide a multi-sensory and experiential learning experience, which can significantly increase a kid’s capacity for learning, according to various studies. Using robots to teach STEAM can also help children understand how technology can be used to solve real-world problems.
4. Why Is STEAM Education Important for Kids?

The importance of STEAM education lies in the many benefits students can get from it:
1. Independent Thinking
STEAM education is not about hand-holding. Students are given room to think, evaluate, and determine how to best achieve their goals and complete projects. The results are not to be measured simply by success or failure; instead it’s the way of thinking that they learned while completing the projects that mattered the most to them.
2. Comprehensive Approach
Many people tend to separate STEM from Art for the supposedly correct reason that art is about being creative and imaginative, while STEM is based on solid numbers and facts. One of the major advantages of STEAM education is its interdisciplinary approach. This also why STEAM education is so important for students no matter what field, art or science, they choose to pursue.
3. Natural Curiosity
STEAM education encourages students to think outside the box and get inspired by more than just STEM-related subjects. This requires teachers not to set limits on students and help them become curious and free to learn all things.
5. From STEM to STEAM – the Difference

The main difference between STEM and STEAM is that STEM symbolizes a modern approach to science and related subjects focusing on solving problems through critical thinking and analytical skills. STEAM education explores the same subjects, but incorporates creative thinking and applied arts into teaching and real situations.
Art is about discovering and creating ingenious ways of problem-solving, integrating principles, and presenting information. By adding the element of art to STEM-based thinking, educators believe that students can use both sides of their brain—analytical and creative— to develop tomorrow’s best thinkers.
6. How to Develop A STEAM Lesson Plan

STEM and STEAM education have extremely wide ranges and can include millions of topics. For teachers or parents who want to teach STEAM, unless they have a thought-out plan, it’s going to be incredibly hard for them to help kids navigate through the world of STEAM. So how do we create a STEAM lesson plan? To put it in a simple way, you can follow these six steps.
5 Tips to Help You Develop a STEAM Lesson Plan
1. Be well-informed
There are lots of STEAM robotic kits you can find, but not all of them are the right fit for your students. You have to first understand what you want them to learn and then do your own research for those specific kits. In the end, you will find one or two kits that you think will benefit them the most.
2. Do It Yourself
It’s all about doing it. Make sure you spend less time lecturing and more time letting kids get their hands dirty. By building a robot, students will learn so much more than you think.
3. Team Work Makes Dream Work
Don’t carry it all by yourself! Ask for help from a teaching assistant or another teacher and invite them to join the class with you in order to keep the class running on schedule. More importantly, you can focus on the teaching part better!
4. A Flexible and Mobile Classroom
As mentioned above, a STEAM class can be very busy, because STEAM education encourages learning through doing and critical discussions among students. A spacious classroom with simple and mobile furniture will be very helpful for you.
5. Try Small Groups
Students will have tons of questions when making a robot, and it’s a teachers’ responsibility to provide guidance. Imagine, if there is a group of 20 students, teachers are surely going to be overwhelmed! So make sure you have 12 students at most in each class.
Examples of STEAM Lesson Plans.
1. The 10 Weeks of Afterschool Maker Program
This program is designed for kids from kindergarten to 5th grade. It will “increase engagement in hands-on exploration and practice of STEM/STEAM in ways that foster excitement, curiosity and interest in learning.”
2. STEAM + Coding Program
Designed for students in grades 3 – 8, this year-long comprehensive program engages students in six creative electronic and coding activities.
3. 10-Week STEAM Program
For 10 weeks, students will be introduced to STEAM through take-home projects using creative materials. The program is best for kindergarteners through 2nd graders.
4. Projects that Tackle Real-World Issues
If your students are a little older, say 6th – 12th grade, and already have some knowledge of STEAM, these projects are going to take them to another level and guide them to build things that can be used in their day-to-day lives.
5. MIT Blossoms – Math and Science Lessons (High School)
High school students are generally in need of more systematic training to help them get ready for college. MIT Blossoms program is designed just for these kids.
6. NASA – STEM Lessons From Space
This NASA-created STEM education program is definitely a one-of-a-kind learning resource that demonstrates STEM knowledge in a real-world setting.
7. STEAM & STEM Robotics Kits for Parents
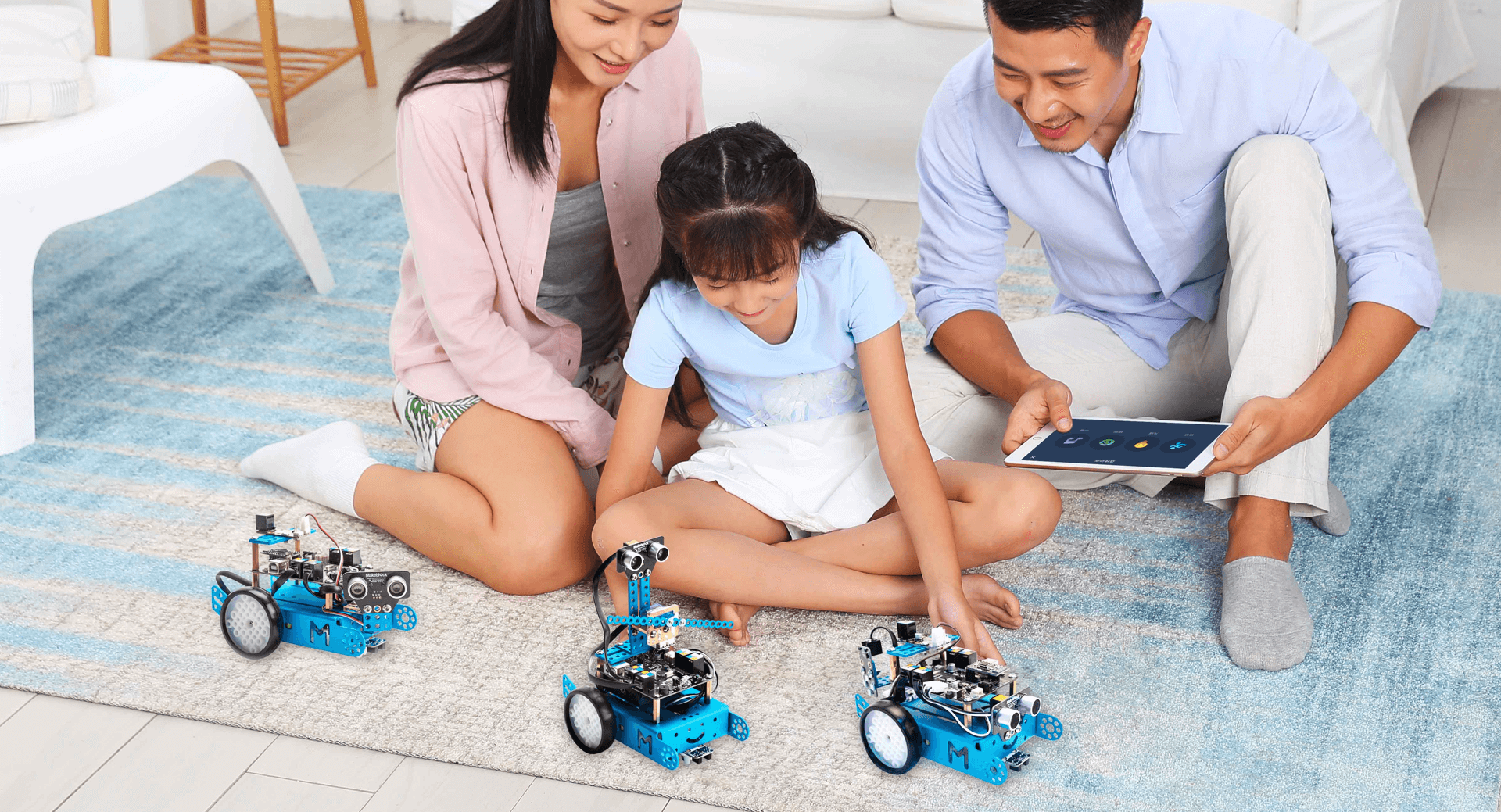
Besides all the online courses and programs you can use, we also recommend using STEM & STEAM robotics kits to add more fun to your kids’ learning journey. Here are the top 10 STEAM robotics kits you might be interested in .
Among all these educational robots, mBot and Codey Rocky simply stand out. Created by the industry leader, Makeblock, they will not let you down. Codey Rocky is a smart robot for beginner coding and AI learning. It combines software learning with hardware creation and helps kids understand commands intuitively and gain rewarding and fun experiences by interacting with the hardware part of Codey Rocky.
mBot is another great STEAM education robot for beginners to learn robot programming. Compared with Codey Rocky, a built-out robotic product, mBot allows children to build a robot from scratch, using a screwdriver and guided by detailed instructions.
What are your questions about STEAM education? Leave a comment below and let us know!